The Power of Mapping Your Emotions
It’s in everyone’s best interest to learn to remove the emotional blinders and identify emotions accurately, both the uncomfortable and the upbeat ones. After all, unpleasant emotions are normal and natural, a fundamental part of being human. Emotions fluctuate on a daily basis, often several times in a given day. If you didn’t experience negative feelings now and then, the positive ones wouldn’t be as noteworthy or joyful; your emotional life would likely be unnaturally narrow. You would also be deprived of the opportunity to glean important insights into yourself. Feelings, both the good and the bad, are silent messages, alerting you to pay attention to something in your personal or professional life, in your behavior, or in the world around you.
Instead of separating emotions into categories such as good or bad, positive or negative, happy or sad, it’s better to view all your emotions as useful information, as “evolutionarily evolved responses that are uniquely appropriate to specific situations,” says Karla McLaren, MEd, author of The Language of Emotions. “When you stop valencing, you’ll learn to empathically respond to what’s actually going on—and you’ll learn how to observe emotions without demonizing them or glorifying them.”

Being able to recognize and express what you’re feeling helps you better understand yourself (leading to greater self-knowledge); validate your emotions and tend to your own emotional needs; and take steps to address those feelings directly by communicating and responding to them effectively. Having emotional self-awareness can motivate you to make healthy changes in your life, take action to improve the world around you, and become more psychologically resilient—that is, better able to cope with crises and rebound from setbacks.
Learning to Unpack Your Emotions
For some people, engaging in free association can clear the cobwebs from their minds, almost like opening the cellar door to a musty basement and letting in light and fresh air. To do this, you might take a break and consider how you’re feeling about what you’re doing, reading, seeing, or thinking every few hours throughout the day. If a general word comes to mind—such as stressed, anxious, or angry—dig deeper and ask yourself what other emotions you might be feeling (maybe fear or annoyance) along with it. If you do this out loud in unedited, private moments, you might find yourself blurting out what you’re really thinking or feeling, revealing the emotions that are taking a lot of energy to keep inside. This is really about unpacking your suitcase of feelings, or untangling the knot of emotions that is taking up space inside you.

When you think about this in the abstract, it can be hard to pinpoint how you’re feeling. You may just see a swirling mass of a feeling quality such as “dread” or “foreboding” rather than recognizing the specific emotions you feel. To get to the root of your feelings, spend five minutes looking at the word cloud below—no more than five so that you don’t have time to filter your responses—and choose the emotions that resonate with your mood-state lately.
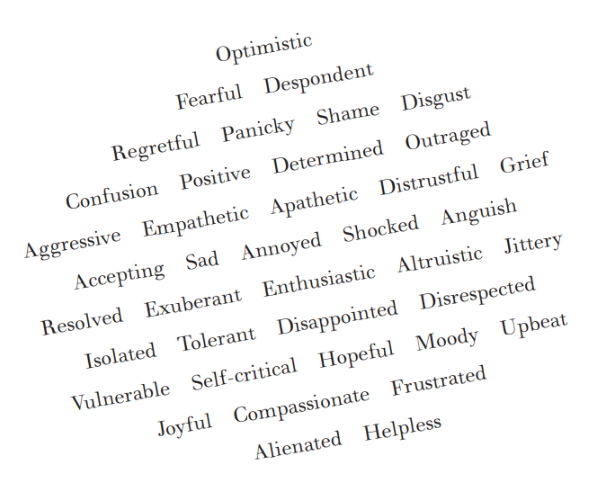
If reviewing these words evokes other feelings for you or if words or phrases that apply to you were not on this word cloud, jot these down in the blank word cloud that follows. Give yourself another five minutes to think about your recent state of mind and jot down phrases, images, or words that occur to you. This is your opportunity to personalize it without any limits or restrictions. If you feel stymied or draw a blank initially, think about your recent responses to current events or situations in your personal life or on the world stage. Try to be as honest as you can by focusing on how you’re really feeling when no one is watching—free-associate without judging, censoring, or revising what you write down.
Once you’ve finished your list, look at the order of the words you wrote down: Did they progress from all negative to increasingly hopeful? Do they portray an internal tension or friction in going back and forth between various feelings? If all the words are positive, consider the possibility that you may be in some degree of denial, focusing only on the window dressing rather than the emotions that lie beneath the surface. Also, consider this: Is there a pattern of shallow, visceral reactions that came out initially, followed by more complex thoughts and feelings? If so, think about whether you’re giving yourself enough time in your life to reflect. If you came out with highly intellectualized words or phrases first, it might suggest that you put on a bit of a facade when engaging with the world, and you might benefit from striving for a deeper engagement or familiarity with your emotions.
This is an excerpt from Emotional Inflammation: Discover Your Triggers and Reclaim Your Equilibrium During Anxious Times by Lise Van Susteren, MD, and Stacey Colino.
Buy your copy of Emotional Inflammation at your favorite bookseller!
Sounds True | Amazon | Barnes & Noble | Bookshop




 Most of us have lost our connection to the mysterious forces at play in the abdominal region, as well as to the appearance, function, and location of the organs and glands within it. We know that this area is responsible for digestion and assimilation, but in most Western cultures, a belly is considered healthy only according to its outer appearance: flat, “cut,” and firm. Good posture is supposed to be chest up, shoulders back, gut in. Emotionally, for many, the belly receives the brunt of our dysfunctional attempts to deal with negative feelings such as anger, fear, or low self-esteem.
Most of us have lost our connection to the mysterious forces at play in the abdominal region, as well as to the appearance, function, and location of the organs and glands within it. We know that this area is responsible for digestion and assimilation, but in most Western cultures, a belly is considered healthy only according to its outer appearance: flat, “cut,” and firm. Good posture is supposed to be chest up, shoulders back, gut in. Emotionally, for many, the belly receives the brunt of our dysfunctional attempts to deal with negative feelings such as anger, fear, or low self-esteem.





